Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment in Shelton, CT
At Advanced Pain and Regenerative Medical Solutions, we utilize the Functional Insulin Therapy (FIT) to treat the root cause and THE MORPH DEVICE (an FDA Cleared Medical Device) to block the painful symptoms while the FIT treatment is in process. Medications and other nonpharmacologic strategies can help to reduce pain and increase quality of life.
Types of Diabetic Neuropathy
- Autonomic neuropathy is a damage to nerves that control internal organs that affects up to 30% of people with diabetes.
- Focal neuropathy often involves a single nerve, such as in the hand, head, torso, or leg.
- Proximal neuropathy is a rare type of nerve damage in the hip, buttock, or thigh.
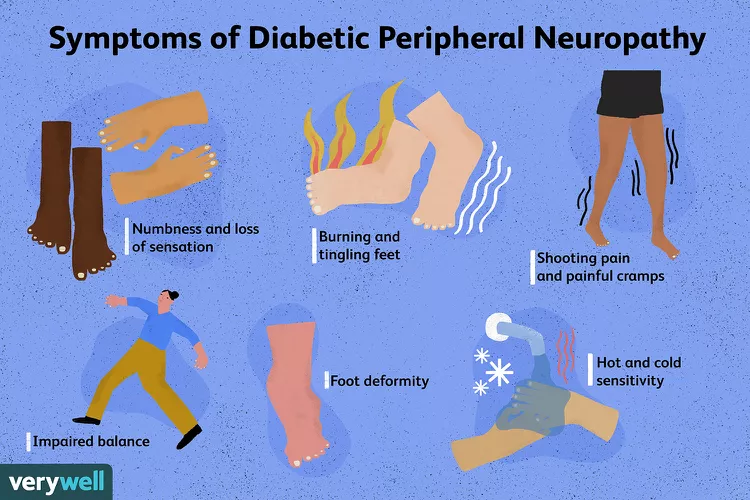
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms
Numbness and Loss of Protective Sensation (LOPS)
Burning and Tingling in Feet
Shooting Pain and Painful Cramps
Loss of Balance
Appearance of Deformity in Foot
Underlying neuropathy and trauma to the foot can lead to deformities of the foot, including hammertoes, bunions, and Charcot foot. Charcot foot affects the bones, joints, and soft tissues of the foot and ankle. Diabetic neuropathy is the most common underlying cause. Sensory, motor, or autonomic neuropathy, trauma, and metabolic abnormalities all contribute to Charcot foot.
Injuries to Foot You Can’t Feel or Explain
Hot and Cold Sensitivity
Nerve damage can interfere with the body’s ability to feel temperature. An inability to feel or sense heat can increase the risk of burns. If you have neuropathy that affects your ability to sense heat, avoid stepping directly into a hot tub; use your forearm to check the water or another part of your body that has sensation. Nerve damage can also reduce blood flow to the feet and hands, making them feel cold or get cold more quickly.
Pain Affects Sleep
Causes of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- Poor glycemic control (as measured by hemoglobin A1C)
- Metabolic factors
- Genetic predisposition
- Having diabetes for a long time
Elevated blood sugars and inadequate blood flow can result in nerve damage in the legs, feet, arms, or hands. High blood glucose can impair the nerves’ ability to transmit signals and cause chemical changes. Elevated sugar can also damage blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients to the nerves. Nerve signaling in neuropathy is disrupted when there is a loss of signals normally sent, inappropriate signaling from nerves, or errors in nerve signaling that distort messages being sent. When nerve damage to the extremities causes damage to multiple peripheral sensory and motor nerves, it is referred to as diabetic polyneuropathy. This can lead to loss of sensation, difficulty in wound healing, and an increased risk of infection. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends that all people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy be checked for other causes of neuropathy, such as exposure to toxins, renal disease, hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), vitamin deficiencies, infections, malignancies, inherited neuropathies, and vasculitis.
Diagnosis
The ADA states that, “Up to 50% of diabetic peripheral neuropathy may be asymptomatic. If not recognized and if preventive foot care is not implemented, patients are at risk for injuries to their insensate feet.” It’s important for people with diabetes to have their feet examined during routine medical visits. Your healthcare professional or certified diabetes care and education specialist can do a foot exam to inspect your feet visually and determine your level of sensation. If an issue exists, further workup may be necessary.
Foot Exams
- Small-fiber function: Pinprick and temperature sensation (Diabetic Neuropathy Device) DND
- Large-fiber function: Vibration perception (Diabetic Neuropathy Device) DND
- Protective sensation: (Diabetic Neuropathy Device) DND
- Inspection and palpation for pedal pulses
Nerve Conduction Studies and EMG
Nerve conduction studies (NCS) and electromyography (EMG) testing may be used to confirm the presence of peripheral neuropathy and assess its pattern and severity, prognosis, and possible treatment options. The ADA suggests that these types of tests are rarely needed except when the clinical features are atypical, and the diagnosis is unclear.
Treatment
At Advanced Pain and Regenerative Medical Solutions, we utilize Functional Insulin Therapy (FIT) to treat the root cause and PENS to block the painful symptoms while the FIT treatment is in process. Medications and other nonpharmacologic strategies can help to reduce pain and increase quality of life.
Foot Care Education
Special Footwear
Therapeutic footwear is recommended for those at high risk who have severe neuropathy, foot deformities, ulcers, callus formation, poor peripheral circulation, or a history of amputation.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
Pain from neuropathy can impact quality of life and lead to feelings of sadness. If you are in pain, you should seek medical treatment. In addition, if you have a wound that won’t heal, notice any deformities, or are experiencing muscle pain, weakness, or cramping, you should contact Advanced Pain and Regenerative Medical Solutions right away.
Summary Diabetic peripheral neuropathy is a very common type of neuropathy in people with diabetes. Screening, early detection, and treatment can help prevent and slow down the progression of the disease. The earliest symptoms include numbness and tingling and may appear gradually. All people with diabetes need to have their feet inspected by a medical professional. In addition, understanding what to look for and how to inspect your own feet is important.

